Cancer radiotherapy, also known as radiation therapy, is a medical treatment that uses high-energy particles or waves, such as X-rays, gamma rays, or protons, to destroy or damage cancer cells. The goal of radiotherapy is to kill cancer cells or slow down their growth, thereby reducing the size of tumors and alleviating symptoms. Radiotherapy is a vital component of cancer treatment, and it is often used in conjunction with other therapies, such as surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy.
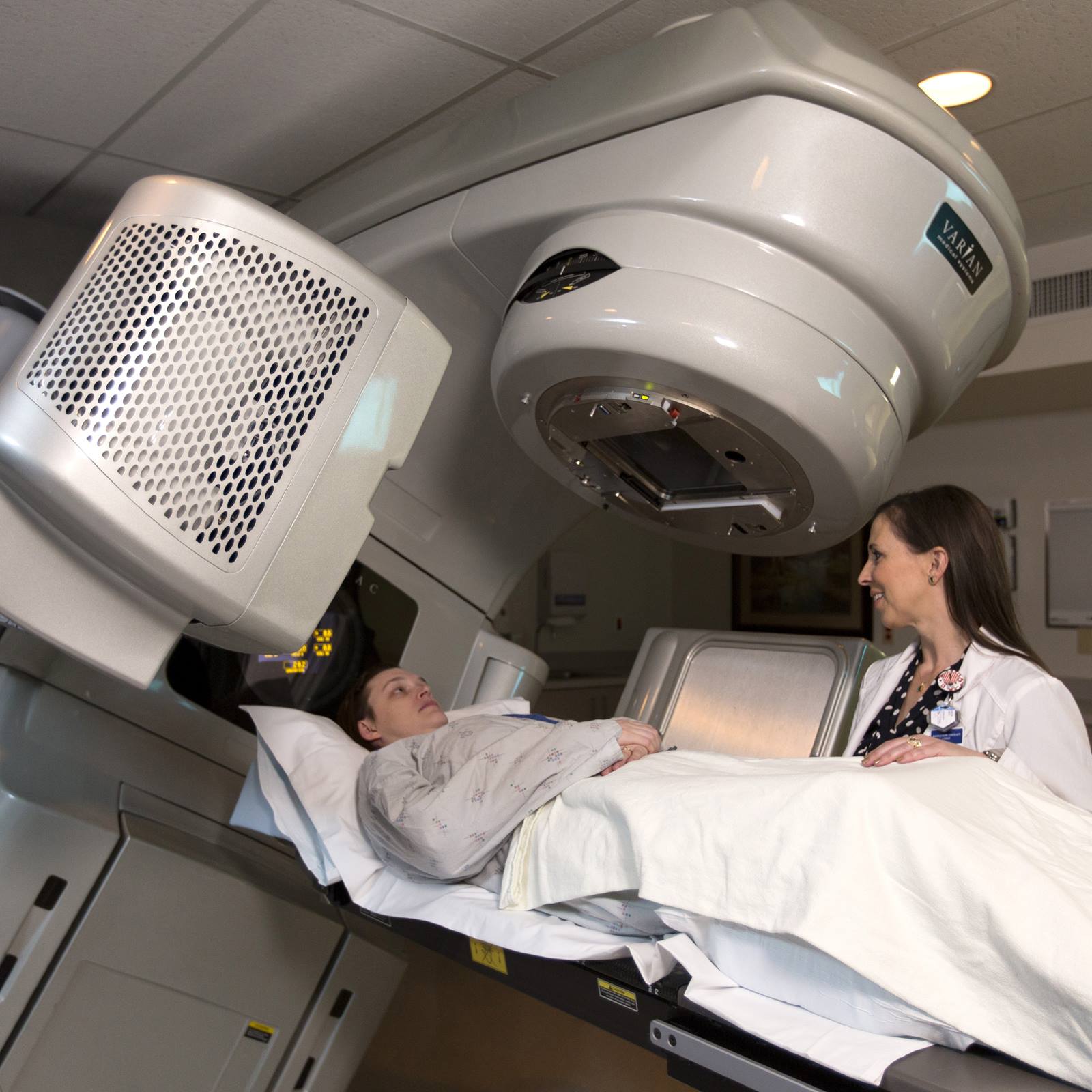
How Does Radiotherapy Work?
Radiotherapy works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. When cancer cells are exposed to radiation, the DNA is damaged, and the cells are unable to repair themselves. As a result, the cancer cells die, and the tumor shrinks. Radiotherapy can be used to treat a wide range of cancers, including breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, and brain tumors.
Types of Radiotherapy
There are several types of radiotherapy, including:
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): This is the most common type of radiotherapy, where a machine outside the body delivers radiation to the tumor.
- Internal Radiation Therapy (Brachytherapy): This type of radiotherapy involves placing a radioactive source inside the body, near the tumor.
- Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT): This is a type of radiotherapy that uses high doses of radiation to treat small tumors.
- Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): This type of radiotherapy uses advanced technology to deliver radiation that is tailored to the shape and size of the tumor.
- Proton Therapy: This type of radiotherapy uses protons instead of X-rays to destroy cancer cells.
Benefits of Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy has several benefits, including:
- Effective in treating a wide range of cancers: Radiotherapy can be used to treat many types of cancer, including brain tumors, breast cancer, lung cancer, and prostate cancer.
- Non-invasive: Radiotherapy is a non-invasive treatment, which means that it does not require surgery.
- Preserves organ function: Radiotherapy can help preserve organ function, reducing the risk of long-term side effects.
- Can be used in combination with other therapies: Radiotherapy can be used in conjunction with other therapies, such as chemotherapy and surgery, to improve treatment outcomes.
Risks and Side Effects of Radiotherapy
While radiotherapy is generally a safe and effective treatment, it can cause side effects, including:
- Fatigue: Radiotherapy can cause fatigue, which can be mild or severe.
- Skin reactions: Radiotherapy can cause skin reactions, such as redness, itching, and dryness.
- Nausea and vomiting: Radiotherapy can cause nausea and vomiting, especially when used to treat cancers in the abdomen or pelvis.
- Hair loss: Radiotherapy can cause hair loss, especially when used to treat cancers in the head or neck.
- Long-term side effects: Radiotherapy can cause long-term side effects, such as infertility, impotence, and secondary cancers.
How is Radiotherapy Planned and Delivered?
Radiotherapy is planned and delivered by a team of healthcare professionals, including radiation oncologists, physicists, and therapists. The planning process involves:
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRI scans, are used to determine the size and location of the tumor.
- Simulation: A simulation is performed to determine the best way to deliver radiation to the tumor.
- Treatment planning: A treatment plan is created to determine the dose and schedule of radiation.
- Treatment delivery: The radiation is delivered to the tumor using a machine, such as a linear accelerator.
FAQs
- What is the success rate of radiotherapy?: The success rate of radiotherapy varies depending on the type of cancer and the stage of the disease. However, radiotherapy can cure many types of cancer, especially when used in conjunction with other therapies.
- How long does radiotherapy treatment take?: The length of radiotherapy treatment varies depending on the type of cancer and the dose of radiation. Treatment can last from a few days to several weeks.
- Can radiotherapy cause secondary cancers?: Yes, radiotherapy can increase the risk of secondary cancers, especially in children and young adults. However, the risk is generally low and depends on the dose and type of radiation.
- Can I work during radiotherapy treatment?: Yes, many people can work during radiotherapy treatment, although it may be necessary to take time off to attend appointments and rest.
- Can I have radiotherapy if I have a pacemaker or other implant?: Yes, but it may be necessary to take precautions to protect the implant from radiation.
Conclusion
Cancer radiotherapy is a vital component of cancer treatment that uses high-energy particles or waves to destroy or damage cancer cells. While radiotherapy can cause side effects, it is generally a safe and effective treatment that can cure many types of cancer. The benefits of radiotherapy include its non-invasive nature, its ability to preserve organ function, and its effectiveness in treating a wide range of cancers. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with cancer, it is essential to discuss the role of radiotherapy in your treatment plan with your healthcare team. With advances in technology and treatment planning, radiotherapy continues to play an important role in the fight against cancer.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into What is Cancer Radiotherapy?. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!