Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that affects the ovaries, which are the female reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs. It is the fifth leading cause of cancer deaths in women, with approximately 22,000 new cases diagnosed each year in the United States alone. The symptoms of ovarian cancer can be subtle and may not appear until the disease is in its advanced stages, making it essential to seek medical attention if any suspicious symptoms persist. In this article, we will delve into the treatment options available for ovarian cancer, exploring the various approaches and therapies that can help manage the disease.
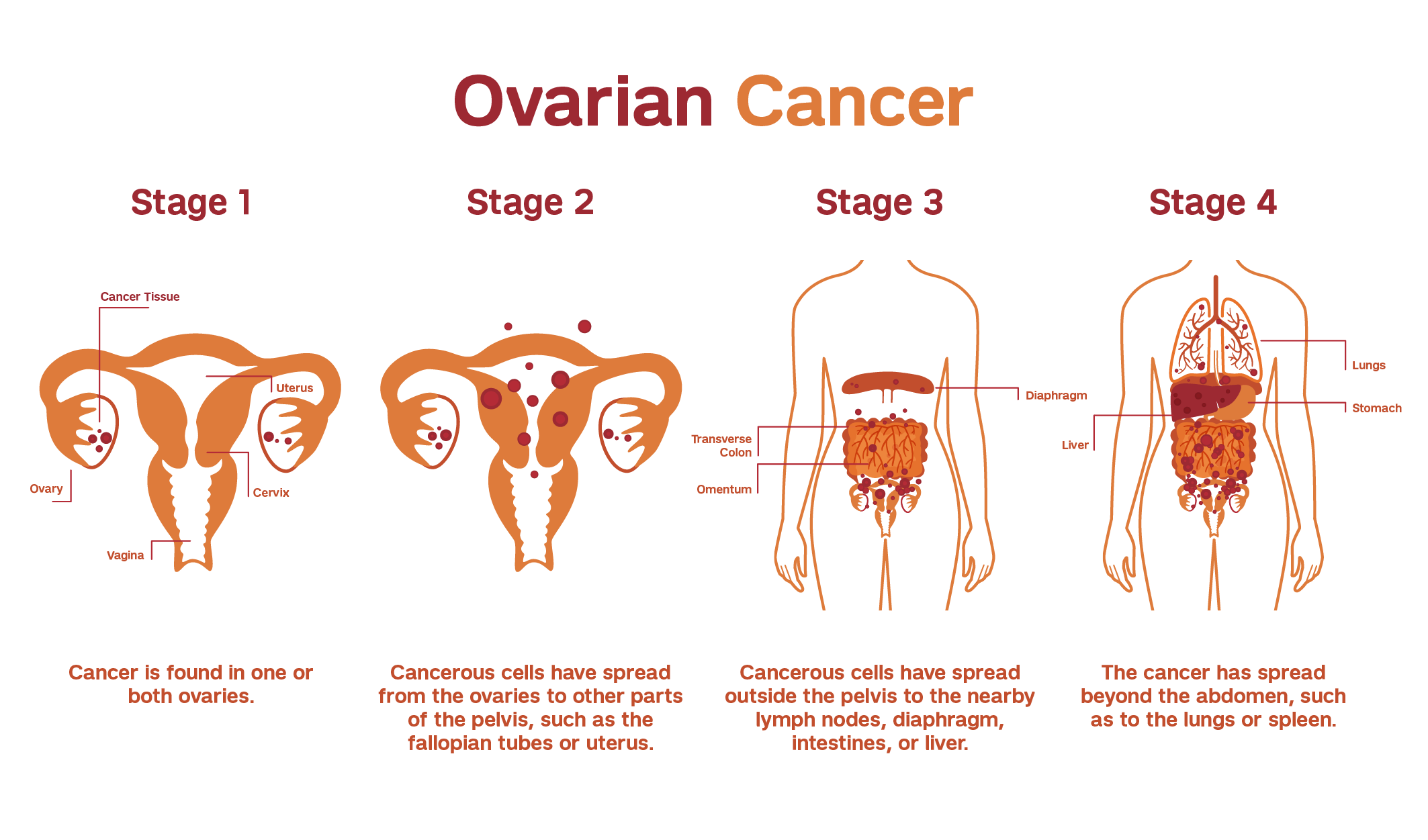
Staging and Diagnosis
Before treatment can begin, it is crucial to determine the stage and extent of the cancer. This involves a combination of physical exams, imaging tests, and blood tests to assess the cancer’s spread and severity. The stages of ovarian cancer are:
- Stage I: Cancer is limited to the ovaries.
- Stage II: Cancer has spread to the pelvis.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread to the abdomen or lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs, such as the liver or lungs.
Treatment Options
The primary treatment for ovarian cancer depends on the stage and type of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences. The following are some of the most common treatment options:
- Surgery: Surgical intervention is often the first line of treatment, aiming to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This may involve a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus), bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (removal of both ovaries and fallopian tubes), or debulking surgery (removal of visible tumor tissue).
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment that uses medications to kill cancer cells. It is often administered through an IV or orally and may be used before or after surgery to reduce tumor size or eliminate remaining cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy involves medications that specifically target cancer cells, reducing harm to healthy cells. These therapies can be used in conjunction with chemotherapy or as a standalone treatment.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It is not commonly used as a primary treatment for ovarian cancer but may be employed to alleviate symptoms or manage recurrence.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy involves medications that block or reduce hormone production, which can fuel the growth of certain types of ovarian cancer.
Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy Regimens
Several chemotherapy and targeted therapy regimens are used to treat ovarian cancer, including:
- Carboplatin and Paclitaxel: A combination of these two medications is commonly used as a first-line treatment for ovarian cancer.
- Bevacizumab (Avastin): A targeted therapy that inhibits angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels that feed cancer cells).
- Olaparib (Lynparza): A targeted therapy that inhibits PARP enzymes, which are involved in DNA repair.
- Niraparib (Zejula): A targeted therapy that also inhibits PARP enzymes.
Clinical Trials and Emerging Therapies
Ovarian cancer research is ongoing, with numerous clinical trials investigating new treatments and therapies. Some promising areas of research include:
- Immunotherapy: Therapies that harness the power of the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Gene Therapy: Therapies that aim to repair or replace faulty genes that contribute to cancer development.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Therapies that use stem cells to promote healthy cell growth and differentiation.
Managing Side Effects and Symptoms
Treatment for ovarian cancer can cause a range of side effects and symptoms, including:
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or weak due to chemotherapy or surgery.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Common side effects of chemotherapy.
- Hair Loss: Chemotherapy can cause hair loss, but this is usually temporary.
- Bowel and Urinary Problems: Surgery or radiation therapy can lead to bowel or urinary issues.
- Menopause: Treatment can induce menopause, leading to symptoms such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness.
To manage these side effects and symptoms, patients can:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on nutrient-rich foods to maintain energy and overall health.
- Exercise Regularly: Gentle exercise, such as yoga or walking, can help alleviate fatigue and improve mood.
- Seek Support: Connect with family, friends, or support groups to cope with emotional and psychological challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the chances of survival for ovarian cancer patients?
A: The 5-year survival rate for ovarian cancer patients is approximately 47%, but this varies depending on the stage and type of cancer.
Q: Can ovarian cancer be prevented?
A: While there is no guaranteed way to prevent ovarian cancer, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and not smoking can reduce the risk.
Q: What are the most common symptoms of ovarian cancer?
A: Symptoms may include bloating, abdominal pain, pelvic pain, difficulty eating or feeling full, and urinary frequency or urgency.
Q: Can ovarian cancer be treated with alternative therapies?
A: Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or herbal supplements, may be used in conjunction with conventional treatments to alleviate symptoms, but they should not replace established treatments.
Q: How often should I undergo screening for ovarian cancer?
A: Women at average risk should undergo annual pelvic exams and report any suspicious symptoms to their healthcare provider. Women at high risk (e.g., those with a family history) may require more frequent screening.
Conclusion
Treating ovarian cancer requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and other treatments. While the disease can be challenging to diagnose and manage, advances in research and therapy have improved outcomes for patients. By understanding the treatment options, managing side effects and symptoms, and staying informed about the latest developments in ovarian cancer research, patients can take an active role in their care and increase their chances of survival. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with ovarian cancer, consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the best course of treatment and explore available resources and support. Remember, early detection and intervention are crucial in the fight against ovarian cancer.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Treating Ovarian Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!