Cancer, a disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells, has been a major health concern for centuries. Despite significant advancements in medical research and treatment options, cancer remains a leading cause of death worldwide. However, with the advent of biotechnology and immunotherapy, a new era in cancer treatment has begun. In this article, we will delve into the world of biotechnology immunotherapy, exploring its nature, applications, and potential in treating cancer.
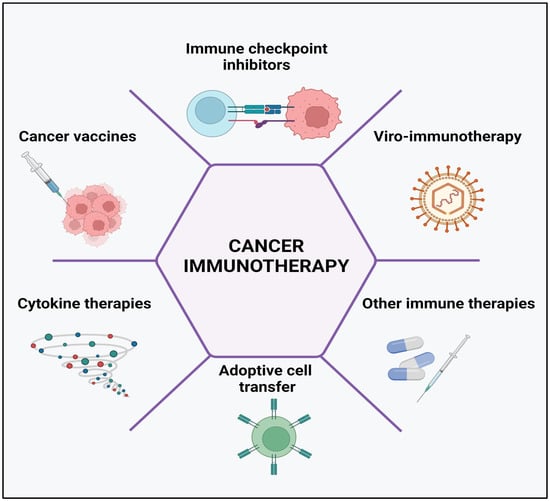
What is Biotechnology Immunotherapy?
Biotechnology immunotherapy, also known as cancer immunotherapy, is a type of treatment that harnesses the power of the immune system to fight cancer. The immune system, composed of various cells, tissues, and organs, plays a vital role in protecting the body against infectious agents and foreign substances. Biotechnology immunotherapy involves the use of biotechnology techniques, such as genetic engineering and cell culture, to enhance the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack cancer cells.
How Does Biotechnology Immunotherapy Work?
Cancer cells often evade the immune system by disguising themselves as normal cells or suppressing the immune response. Biotechnology immunotherapy aims to overcome these obstacles by using various strategies, including:
- Cancer vaccines: These vaccines stimulate the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells by introducing antigens, substances that trigger an immune response.
- Monoclonal antibodies: These laboratory-produced antibodies are designed to bind to specific proteins on cancer cells, marking them for destruction by the immune system.
- Checkpoint inhibitors: These treatments release the brakes on the immune system, allowing it to attack cancer cells more effectively.
- Adoptive T-cell therapy: This involves removing T-cells, a type of immune cell, from the patient’s blood, modifying them to recognize cancer cells, and reinfusing them into the body.
Types of Biotechnology Immunotherapy
Several types of biotechnology immunotherapy are being developed and used to treat various types of cancer, including:
- CAR-T cell therapy: A type of adoptive T-cell therapy, where T-cells are genetically engineered to produce chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) that recognize and bind to specific proteins on cancer cells.
- Checkpoint inhibitor therapy: Treatments that target checkpoint proteins, such as PD-1 and CTLA-4, to enhance the immune response against cancer cells.
- Cancer vaccine therapy: Vaccines that stimulate the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells, such as sipuleucel-T (Provenge) for prostate cancer.
Benefits of Biotechnology Immunotherapy
Biotechnology immunotherapy offers several benefits over traditional cancer treatments, including:
- Targeted treatment: Immunotherapy targets specific cancer cells, reducing harm to healthy cells.
- Long-term effects: Immunotherapy can provide long-term protection against cancer, with some patients experiencing complete remission.
- Combination therapy: Immunotherapy can be used in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy, to enhance its effectiveness.
- Personalized medicine: Immunotherapy can be tailored to individual patients, taking into account their unique genetic profiles and immune systems.
Challenges and Limitations
While biotechnology immunotherapy holds great promise, there are several challenges and limitations to its widespread adoption, including:
- Cost: Immunotherapy can be expensive, making it inaccessible to many patients.
- Side effects: Immunotherapy can cause side effects, such as fatigue, rash, and diarrhea, which can be severe in some cases.
- Limited understanding: The immune system is complex, and the mechanisms of immunotherapy are not yet fully understood, making it challenging to predict patient outcomes.
- Regulatory frameworks: Regulatory frameworks for immunotherapy are still evolving, which can create uncertainty for developers and patients.
Future Directions
As research continues to advance, we can expect to see significant improvements in biotechnology immunotherapy, including:
- Combination regimens: Development of combination regimens that pair immunotherapy with other treatments, such as chemotherapy and targeted therapy.
- Biomarkers: Identification of biomarkers that can predict patient response to immunotherapy, allowing for more personalized treatment.
- Next-generation immunotherapies: Development of new immunotherapies, such as CAR-NK cell therapy and tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy.
FAQs
- What is the difference between immunotherapy and chemotherapy?
Immunotherapy works by stimulating the immune system to attack cancer cells, while chemotherapy uses chemical agents to kill cancer cells directly. - Is immunotherapy suitable for all types of cancer?
No, immunotherapy is not suitable for all types of cancer. It is most effective for cancers that are immunogenic, meaning they can stimulate an immune response. - What are the potential side effects of immunotherapy?
Immunotherapy can cause side effects, such as fatigue, rash, diarrhea, and inflammation, which can be severe in some cases. - How long does it take to see the effects of immunotherapy?
The effects of immunotherapy can take time to develop, with some patients experiencing a response within weeks or months, while others may take longer. - Is immunotherapy a cure for cancer?
Immunotherapy is not a cure for cancer, but it can provide long-term protection against cancer and improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Biotechnology immunotherapy represents a significant advancement in cancer treatment, offering a new paradigm for fighting this devastating disease. By harnessing the power of the immune system, immunotherapy has the potential to provide long-term protection against cancer and improve patient outcomes. While challenges and limitations remain, ongoing research and development are expected to overcome these hurdles, making immunotherapy an increasingly viable option for patients with cancer. As we continue to unravel the complexities of the immune system and cancer biology, we can expect to see significant improvements in biotechnology immunotherapy, bringing new hope to patients and their families.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Biotechnology: Unlocking the Potential of Immunotherapy in Cancer Treatment. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!