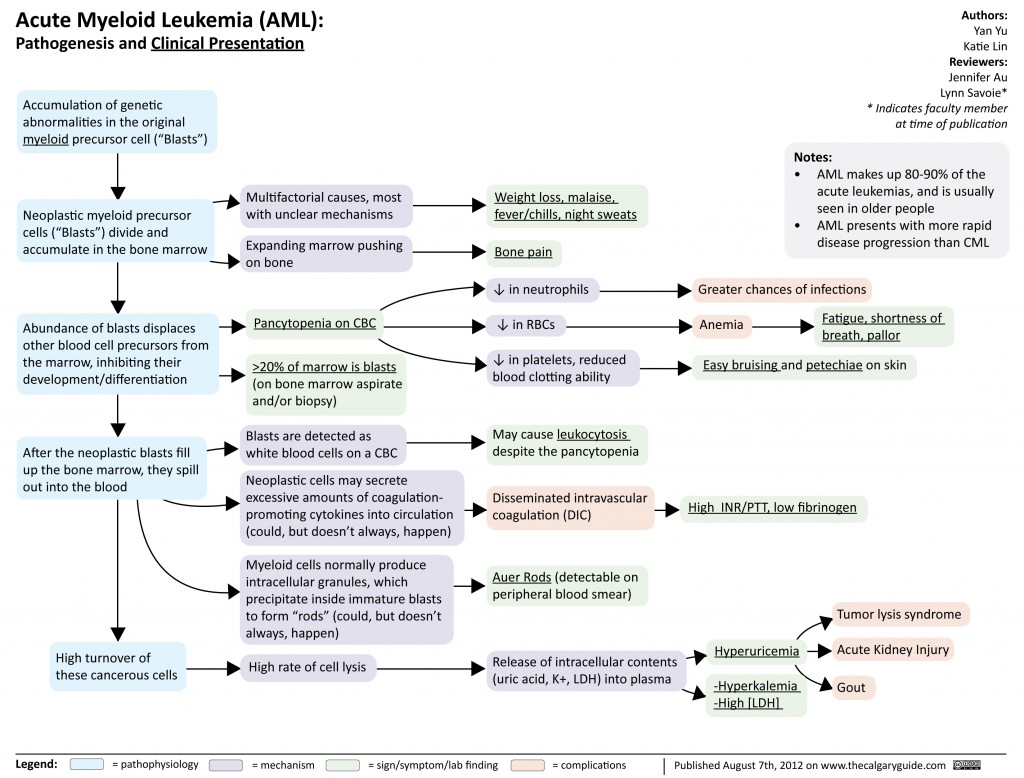
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is a type of blood cancer that affects the bone marrow, blood, and other parts of the body. It is characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal white blood cells, known as myeloid cells, which accumulate in the bone marrow and interfere with the production of normal blood cells. AML is the most common type of acute leukemia in adults, and its treatment can be challenging due to its aggressive nature.
Causes and Risk Factors of AML
The exact cause of AML is not known, but certain risk factors have been identified. These include:
- Exposure to high levels of radiation
- Previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy
- Genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome
- Certain chemicals, such as benzene
- Age: AML is more common in adults over the age of 50
- Smoking: Smoking is a known risk factor for AML
Symptoms of AML
The symptoms of AML can vary, but common signs include:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Weight loss
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Fever
- Infections
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Bone or joint pain
Diagnosis of AML
The diagnosis of AML typically involves a series of tests, including:
- Blood tests: To check for abnormal white blood cells
- Bone marrow biopsy: To examine the bone marrow for cancer cells
- Imaging tests: Such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to check for signs of cancer in other parts of the body
- Cytogenetic analysis: To examine the chromosomes of the cancer cells
Treatment Options for AML
The treatment of AML depends on several factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, and the specific characteristics of the cancer cells. The most common treatment options for AML include:
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is the primary treatment for AML. It involves the use of medications to kill cancer cells. The most common chemotherapy regimen for AML is a combination of cytarabine (Ara-C) and anthracycline (such as daunorubicin or idarubicin).
- Stem Cell Transplantation: Stem cell transplantation is a procedure in which healthy stem cells are infused into the patient’s body to replace the cancerous bone marrow. This can be an allogeneic transplant (using donor stem cells) or an autologous transplant (using the patient’s own stem cells).
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy involves the use of medications that specifically target cancer cells, reducing the harm to healthy cells. Examples of targeted therapies for AML include FLT3 inhibitors and IDH2 inhibitors.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy is a type of treatment that uses the patient’s immune system to fight cancer. It involves the use of medications that stimulate the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
New and Emerging Treatments for AML
Several new and emerging treatments are being developed for AML, including:
- CAR-T Cell Therapy: CAR-T cell therapy involves the use of genetically modified T cells to recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Gene Therapy: Gene therapy involves the use of medications to modify the genes of cancer cells, making them more susceptible to treatment.
- Epigenetic Therapy: Epigenetic therapy involves the use of medications to modify the epigenetic markers of cancer cells, making them more susceptible to treatment.
Side Effects of AML Treatment
The side effects of AML treatment can be significant, and may include:
- Fatigue: Fatigue is a common side effect of chemotherapy and other treatments for AML.
- Infection: Infection is a major risk for patients with AML, particularly those undergoing chemotherapy or stem cell transplantation.
- Hair Loss: Hair loss is a common side effect of chemotherapy.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Nausea and vomiting are common side effects of chemotherapy.
- Mouth Sores: Mouth sores are a common side effect of chemotherapy.
Management of Side Effects
The management of side effects is an important part of AML treatment. This may include:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be used to prevent or treat infections.
- Growth Factor Support: Growth factors, such as filgrastim, may be used to stimulate the production of healthy blood cells.
- Pain Management: Pain management medications, such as morphine, may be used to manage pain.
- Anti-Nausea Medications: Anti-nausea medications, such as ondansetron, may be used to manage nausea and vomiting.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the prognosis for AML?
The prognosis for AML depends on several factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, and the specific characteristics of the cancer cells. With treatment, the overall five-year survival rate for AML is around 25-30%. - Is AML curable?
AML is a potentially curable disease, particularly in patients who are able to undergo stem cell transplantation. However, the disease can be challenging to treat, and relapse is a major risk. - What is the role of family history in AML?
Family history can play a role in AML, particularly in patients with a history of Down syndrome or other genetic disorders. - Can AML be prevented?
There is no known way to prevent AML, but avoiding exposure to radiation and certain chemicals may reduce the risk. - What is the role of clinical trials in AML treatment?
Clinical trials play a critical role in the development of new treatments for AML, and patients may be eligible to participate in these trials.
Conclusion
Acute Myeloid Leukemia is a complex and challenging disease to treat. While the prognosis for AML can be poor, advances in treatment options, including chemotherapy, stem cell transplantation, and targeted therapy, have improved outcomes for many patients. New and emerging treatments, such as CAR-T cell therapy and gene therapy, offer hope for even better outcomes in the future. It is essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan and to manage side effects effectively. With the right treatment and support, many patients with AML can achieve remission and live long, healthy lives.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Understanding the Disease and its Treatment Options. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!