A tumor is a mass of tissue that forms when cells in a specific area of the body grow and multiply uncontrollably. Tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and they can occur in almost any part of the body. In this article, we will delve into the world of tumors, exploring their causes, symptoms, types, and treatment options.
What Causes Tumors?
Tumors occur when there is an abnormal growth of cells in the body. This can happen due to a variety of reasons, including:
- Genetic mutations: Changes in the DNA of cells can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, resulting in tumor formation.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as human papillomavirus (HPV), can increase the risk of tumor development.
- Exposure to carcinogens: Substances like tobacco, radiation, and certain chemicals can damage cell DNA, leading to tumor growth.
- Hormonal imbalances: Hormonal changes can stimulate cell growth, increasing the risk of tumor development.
- Weakened immune system: A compromised immune system can make it harder for the body to fight off abnormal cell growth.
Types of Tumors
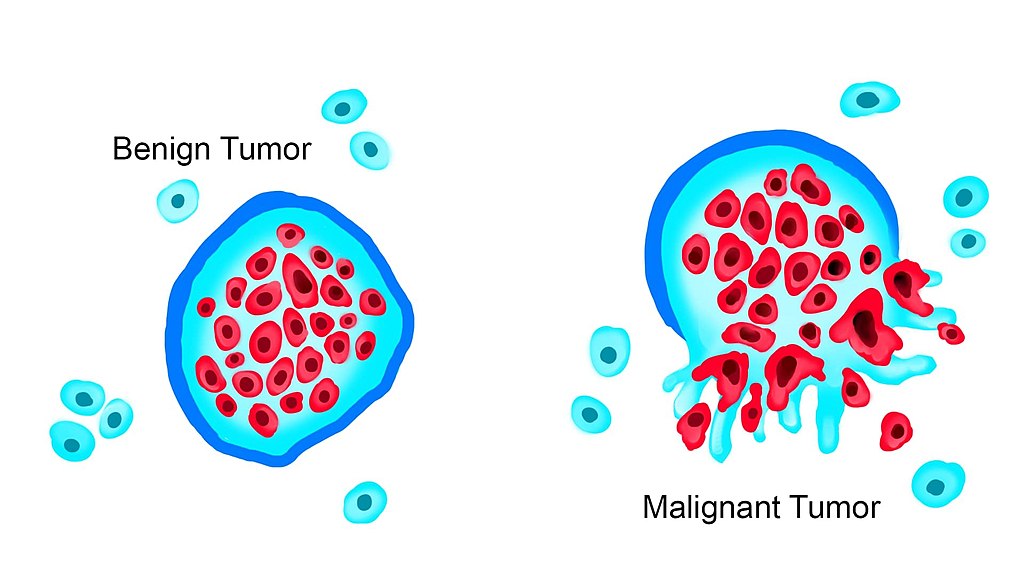
Tumors can be broadly classified into two categories: benign and malignant.
- Benign tumors: These are non-cancerous tumors that do not invade surrounding tissues or spread to other parts of the body. Benign tumors can still cause problems, such as compressing nearby organs or causing pain.
- Malignant tumors: These are cancerous tumors that can invade surrounding tissues and spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
Common Types of Tumors
Some common types of tumors include:
- Brain tumors: Tumors that form in the brain, including glioblastoma, meningioma, and acoustic neuroma.
- Breast tumors: Tumors that form in the breast tissue, including breast cancer and fibroadenoma.
- Lung tumors: Tumors that form in the lungs, including lung cancer and hamartoma.
- Colon tumors: Tumors that form in the colon, including colon cancer and polyps.
- Skin tumors: Tumors that form in the skin, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Symptoms of Tumors
The symptoms of tumors can vary depending on the location and type of tumor. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain: Tumors can cause pain, especially if they are pressing on surrounding tissues or nerves.
- Swelling: Tumors can cause swelling or lumps in the affected area.
- Weight loss: Malignant tumors can cause weight loss, fatigue, and loss of appetite.
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits: Tumors in the colon or urinary tract can cause changes in bowel or bladder habits.
- Unusual bleeding or discharge: Tumors can cause unusual bleeding or discharge, such as vaginal bleeding or coughing up blood.
Diagnosing Tumors
Diagnosing tumors typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and laboratory tests. Some common diagnostic tests include:
- Biopsy: A sample of tissue is removed from the tumor and examined under a microscope to determine if it is benign or malignant.
- Imaging tests: Tests such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and PET scans can help identify the location and size of the tumor.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can help identify markers of cancer, such as CA-125 for ovarian cancer.
Treating Tumors
The treatment of tumors depends on the type and location of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health. Some common treatment options include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor, either alone or in combination with other treatments.
- Chemotherapy: The use of medications to kill cancer cells, either orally or intravenously.
- Radiation therapy: The use of high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: The use of medications that target specific molecules involved in cancer growth and development.
- Immunotherapy: The use of medications that stimulate the immune system to attack cancer cells.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the difference between a benign and malignant tumor?
A benign tumor is non-cancerous, while a malignant tumor is cancerous and can invade surrounding tissues and spread to other parts of the body. - Can tumors be prevented?
While some tumors cannot be prevented, reducing exposure to carcinogens, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and getting regular screenings can help reduce the risk of tumor development. - What are the chances of surviving a malignant tumor?
The chances of surviving a malignant tumor depend on the type and location of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health and response to treatment. - Can tumors be treated with alternative therapies?
While some alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and herbal supplements, may be used in conjunction with conventional treatment, there is no scientific evidence to support their use as a replacement for conventional treatment. - Can tumors recur after treatment?
Yes, tumors can recur after treatment, especially if the tumor was not completely removed or if cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body.
Conclusion
Tumors are abnormal growths of tissue that can occur in almost any part of the body. While some tumors are benign, others are malignant and can invade surrounding tissues and spread to other parts of the body. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for tumors is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, getting regular screenings, and seeking medical attention if symptoms persist, individuals can reduce their risk of tumor development and improve their chances of survival. If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with a tumor, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment and develop a plan for recovery.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Tumors: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!